Vietnam-Indonesia Trade Relations: Top Vietnam Imports from Indonesia & Latest Bilateral Trade Insights
Explore Vietnam–Indonesia trade relations, top Vietnam imports from Indonesia, latest trade data, key sectors, trends, & future bilateral trade outlook.

Introduction: Why Vietnam–Indonesia Trade Matters More Than Ever
Vietnam and Indonesia are two of Southeast Asia’s most influential economies. Together, they account for over 380 million people, large domestic markets, and a combined GDP exceeding US$2 trillion. As founding members of ASEAN and active participants in regional trade agreements, both countries have steadily strengthened economic ties over the past decade. According to the latest Vietnam import data & Indonesia export data, the total value of Vietnam imports from Indonesia reached $10.49 billion in 2024, a 5% increase from the previous year. The total value of Vietnam-Indonesia trade accounted for $16.66 billion in 2024 and a record $17.2 billion in 2025, as per the Vietnam customs data.
Vietnam is ranked fourth among Indonesia's trading partners, while Indonesia is Vietnam's third-largest trading partner in ASEAN, according to global trade data. By 2024–25, Vietnam–Indonesia trade has entered a new phase. Trade volumes are at record highs, supply chains are more integrated, and both governments have elevated their relationship to a Comprehensive Strategic Partnership, reflecting not just commercial interests but long-term economic coordination.
At the center of this relationship lies a critical dynamic: Vietnam’s heavy and growing imports from Indonesia, particularly in energy, raw materials, and industrial inputs. These imports support Vietnam’s rapid industrialization, infrastructure expansion, and manufacturing exports. This article provides a deep, data-driven analysis of:
-
The scale and structure of Vietnam–Indonesia bilateral trade
-
Vietnam’s top imports from Indonesia, by value and sector
-
Recent trends shaping trade in 2024–25
-
Trade balance dynamics and policy implications
-
What lies ahead for both economies
Overview of Vietnam–Indonesia Bilateral Trade
Rapid Growth in Trade Value Historically
Bilateral trade between Vietnam and Indonesia has expanded dramatically:
-
2020: Approximately US$8.1 billion
-
2022: Around US$14 billion
-
2024: Roughly US$16.7 billion
-
Early 2025: Continued double-digit year-on-year growth
In just four years, total Vietnam-Indonesia trade has more than doubled, making Indonesia one of Vietnam’s largest trading partners within ASEAN and Vietnam one of Indonesia’s key export destinations in mainland Southeast Asia.
Trade Momentum in 2025
Early trade data from January–February 2025 indicates:
-
Total bilateral trade growth of over 14% year-on-year
-
Monthly trade flows consistently exceeding US$1 billion
-
Strong import demand from Vietnam, especially for coal, metals, and vehicles
This momentum reflects stable macroeconomic conditions in both countries and continued industrial expansion in Vietnam.
Trade Volume Reaches New Heights
Trade between Vietnam and Indonesia has grown sharply:
-
In 2024, total bilateral trade surged to roughly US$16.7 billion, nearly doubling from just over US$8 billion in 2020.
-
In early 2025, trade momentum continued with a 14.6% year-on-year increase in total exchange during the first two months of the year.
Indonesia ranks as one of Vietnam’s largest ASEAN trading partners, and Vietnam also figures among Indonesia’s top ASEAN trade allies, reflecting deepening economic integration.
Top Goods Vietnam Imports from Indonesia: What Does Vietnam Import from Indonesia?
Vietnam primarily imports a diverse range of goods from Indonesia, showcasing a strong trade relationship between the two nations. Some of the top goods that Vietnam imports from Indonesia include crude oil, coal, coffee, machinery, and electrical equipment. This trade partnership is mutually beneficial, with both countries contributing to each other's economies through these imports. The top 10 products that Vietnam imports from Indonesia, as per the Vietnam shipment data for 2025, include:
1. Mineral Fuels & Oils (HS Code 27): $2.53 Billion
Mineral fuels and oils are one of the leading commodities that Vietnam imports from Indonesia. With a whopping $2.53 billion worth of imports, these products play a crucial role in Vietnam's energy sector. Indonesia, being rich in natural resources, has been a reliable supplier of mineral fuels and oils to Vietnam, meeting the country's energy demands. Mineral fuels, primarily coal, represent Vietnam’s largest import category from Indonesia, as per the customs data on Vietnam coal imports from Indonesia by HS code. These imports are essential for sustaining Vietnam’s fast-growing energy demand, especially as industrial production and urban electricity consumption continue to rise. Indonesia’s role as a major supplier is reinforced by:
-
Competitive export pricing
-
Geographic proximity and efficient shipping routes
-
Reliable, large-scale coal output
Mineral fuel imports are mainly used for:
-
Coal-fired power generation
-
Cement manufacturing
-
Heavy industrial processes
Despite Vietnam’s long-term transition toward renewable energy, coal and other mineral fuels will remain critical in the short to medium term.
2. Vehicles (HS Code 87): $1.37 Billion
Vehicles are another significant category of goods that Vietnam imports from Indonesia. With imports amounting to $1.37 billion, Vietnam relies on Indonesia for a variety of vehicles, including automobiles, motorcycles, and parts. This shows the strong automotive trade between the two countries, highlighting Indonesia's expertise in the manufacturing of vehicles. Vehicle imports from Indonesia have grown rapidly, reflecting Vietnam’s:
-
Rising middle class
-
Expanding urban populations
-
Increasing demand for personal and commercial transport
Indonesia is a leading automotive manufacturing hub within ASEAN, supplying Vietnam with:
-
Passenger cars
-
Commercial trucks and vans
-
Specialized and utility vehicles
ASEAN free trade agreements reduce tariffs, making Indonesian vehicles more affordable and competitive in Vietnam’s market.
3. Iron & Steel (HS Code 72): $1.26 Billion
Iron and steel products are essential raw materials that Vietnam imports from Indonesia. With imports worth $1.26 billion, these products are crucial for Vietnam's construction and manufacturing industries. Indonesia's iron and steel sector has been a key contributor to meeting Vietnam's demand for these materials. Iron and steel remain fundamental to Vietnam’s:
-
Infrastructure development
-
Construction sector
-
Machinery and equipment manufacturing
Although Vietnam has expanded its domestic steel capacity, imports from Indonesia are still necessary due to:
-
Cost advantages
-
Availability of specific grades and semi-finished forms
-
Demand from large-scale public and private infrastructure projects
As urbanization and industrialization continue, steel imports are expected to stay strong.
4. Animal or Vegetable Fats & Oils (HS Code 15): $700.17 Million
Animal or vegetable fats and oils are also among the top goods that Vietnam imports from Indonesia, as per the data on Vietnam oil imports from Indonesia by HS code. With imports totaling $700.17 million, these products play a vital role in Vietnam's food processing and culinary industries. Indonesia's rich agricultural resources make it a preferred supplier of fats and oils to Vietnam. This category is dominated by palm oil, a key Indonesian export. Vietnam relies on these imports for:
-
Cooking oils and food processing
-
Confectionery and packaged foods
-
Industrial applications such as cosmetics, soaps, and biofuels
Imports support:
-
Domestic consumption
-
Food manufacturing
-
Re-export and processing industries
Growth in Vietnam’s food and consumer goods sectors continues to underpin demand.
5. Copper & Articles Thereof (HS Code 74): $623.73 Million
Copper and articles thereof are important commodities that Vietnam sources from Indonesia. With imports valued at $623.73 million, these products are crucial for Vietnam's electrical and electronic industries. Indonesia's copper and related products are known for their quality and reliability, making them sought after by Vietnamese businesses. Copper imports play a vital role in Vietnam’s expanding manufacturing base, particularly in:
-
Electrical wiring and cables
-
Electronics and semiconductors
-
Industrial machinery and components
As Vietnam strengthens its position as a regional electronics and electrical equipment hub, demand for refined copper and copper-based products from Indonesia continues to increase.
6. Electrical Machinery & Equipment (HS Code 85): $490.92 Million
Electrical machinery and equipment are key goods that Vietnam imports from Indonesia. With imports amounting to $490.92 million, these products are vital for Vietnam's technology and manufacturing sectors. Indonesia's expertise in producing electrical equipment makes it a valuable trading partner for Vietnam in this category. Vietnam’s Electrical machinery imports from Indonesia include:
-
Power equipment
-
Electrical components
-
Consumer and industrial electronics
These products support Vietnam’s:
-
Electronics assembly industry
-
Renewable energy infrastructure
-
Manufacturing automation
This category reflects Vietnam’s shift toward higher-value industrial production.
7. Fish & Seafood (HS Code 03): $332.48 Million
Fish and seafood are popular products that Vietnam imports from Indonesia. With imports worth $332.48 million, these products are important for Vietnam's food and beverage industry. Indonesia's abundant marine resources make it a major supplier of fish and seafood to Vietnam. Indonesia is a major supplier of fish and seafood products to Vietnam, which are used for:
-
Domestic consumption
-
Seafood processing
-
Re-export after value-added processing
Vietnam’s strong seafood export industry depends on imported raw materials to maintain a consistent supply and product variety.
8. Paper & Paperboard (HS Code 48): $327.53 Million
Paper and paperboard products are essential goods that Vietnam imports from Indonesia. With imports totaling $327.53 million, these products are crucial for Vietnam's packaging and printing industries. Indonesia's high-quality paper products are favored by Vietnamese businesses for their reliability. Paper and paperboard imports are driven largely by:
-
Packaging needs for exports
-
Consumer goods labeling
-
Printing and publishing
Vietnam’s export-oriented manufacturing sector, especially electronics, textiles, and food products, relies heavily on imported packaging materials.
9. Nuclear Reactors & Machinery (HS Code 84): $277.81 Million
Nuclear reactors and machinery are significant goods that Vietnam sources from Indonesia. With imports valued at $277.81 million, these products are essential for Vietnam's energy and manufacturing sectors. Indonesia's expertise in nuclear technology makes it a valuable supplier for Vietnam in this category. This category covers a broad range of industrial machinery, including:
-
Boilers and mechanical equipment
-
Manufacturing and processing machinery
-
Industrial production systems
These imports are essential for:
-
Factory expansion
-
Productivity improvements
-
Technology upgrading across industries
10. Plastics & Articles Thereof (HS Code 39): $249.58 Million
Plastics and articles thereof are key commodities that Vietnam imports from Indonesia. With imports amounting to $249.58 million, these products are crucial for Vietnam's plastic and packaging industries. Indonesia's high-quality plastic products are in demand in Vietnam, driving trade in this category. Vietnam’s Plastic imports from Indonesia include:
-
Plastic resins and raw materials
-
Packaging materials
-
Industrial plastic components
They are widely used in:
-
Consumer goods manufacturing
-
Electronics assembly
-
Automotive and household products
As Vietnam’s manufacturing ecosystem expands, plastics remain a core input material.
Vietnam’s Trade Balance with Indonesia
Persistent Trade Deficit
Vietnam has traditionally run a trade deficit with Indonesia, driven by its reliance on Indonesian raw materials and energy products.
-
2024 trade deficit was around US$4.3 billion
-
Imports accounted for roughly 60%–63% of total bilateral trade
-
Exports, while growing, lag behind import growth in absolute terms
In January 2025 alone, Vietnam imported about US$690 million worth of goods from Indonesia while exporting around US$437 million, resulting in a monthly deficit exceeding US$250 million.
Is the Deficit a Concern?
From a structural perspective, the deficit is not inherently negative:
-
Imports are largely productive inputs (coal, steel, machinery)
-
These inputs support Vietnam’s export-oriented manufacturing sectors
-
Rising exports to other global markets offset the bilateral deficit
However, policymakers remain focused on export diversification and value-added production to improve balance over time.
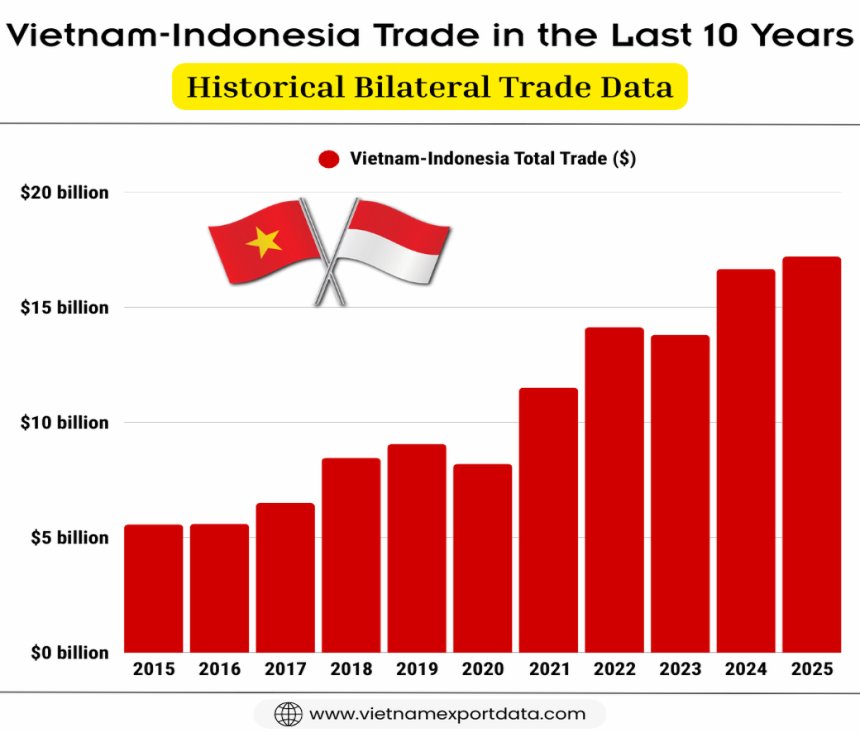
Vietnam-Indonesia Trade in the Last 10 Years: Historical Bilateral Trade Data
|
Year of Trade |
Vietnam-Indonesia Total Trade ($) |
|
2015 |
$5.57 billion |
|
2016 |
$5.60 billion |
|
2017 |
$6.50 billion |
|
2018 |
$8.46 billion |
|
2019 |
$9.06 billion |
|
2020 |
$8.20 billion |
|
2021 |
$11.51 billion |
|
2022 |
$14.13 billion |
|
2023 |
$13.80 billion |
|
2024 |
$16.66 billion |
|
2025 |
$17.20 billion |
Import Trends in Early 2025
Data from late 2024 and early 2025 shows several notable trends:
-
Monthly imports from Indonesia frequently range between US$950 million and US$1.15 billion
-
Coal remains the top import every month
-
Strong seasonal demand for metals and fats during manufacturing peaks
-
Continued growth in automobile imports
These patterns indicate stable demand rather than short-term volatility.
Vietnam’s Exports to Indonesia: A Complementary Flow
Although imports dominate the relationship, Vietnam’s exports to Indonesia have also expanded.
Key Export Categories
-
Rice: US$740 million
-
Textiles and garments: US$550 million combined
-
Chemicals and plastics: US$550 million
-
Machinery and equipment: US$490 million
-
Electronics and components: $450 million
-
Transport equipment and parts: US$390 million
Vietnam’s exports reflect its strengths in:
-
Labor-intensive manufacturing
-
Processed agricultural products
-
Electronics assembly
While export growth has been strong overall, some categories experienced short-term declines in early 2025 due to inventory adjustments and weaker demand in specific segments.
Policy Framework Supporting Trade Growth
ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA)
Tariff reductions under AFTA have made bilateral trade more cost-efficient, particularly for:
-
Vehicles
-
Processed foods
-
Manufactured goods
Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP)
RCEP has further streamlined:
-
Rules of origin
-
Customs procedures
-
Supply chain integration
This has encouraged firms to source intermediate goods from within the region, benefiting Indonesia-Vietnam trade.
Strategic Drivers Behind the Trade Relationship
1. Complementary Economies
Indonesia supplies:
-
Energy resources
-
Raw materials
-
Basic industrial inputs
Vietnam specializes in:
-
Manufacturing
-
Assembly
-
Export-oriented production
This complementarity reduces direct competition and encourages trade.
2. Geographic Proximity
Short shipping routes lower logistics costs and support just-in-time supply chains.
3. Expanding Consumer Markets
Both countries have young populations and rising incomes, driving demand for vehicles, food products, and manufactured goods.
4. Investment Linkages
Vietnamese and Indonesian firms are increasingly investing in each other’s markets, reinforcing trade flows.
Challenges and Risks
Despite strong growth, challenges remain:
-
Persistent trade imbalance
-
Exposure to energy price volatility
-
Agricultural trade sensitivity to domestic policy shifts
-
Regulatory and standards alignment
Addressing these issues will require continued dialogue and policy coordination.
Outlook for 2026 and Beyond
Looking ahead:
-
Both countries aim to push bilateral trade toward US$18–20 billion.
-
Energy, metals, and automotive trade will remain core pillars.
-
Greater cooperation is expected in green energy, electric vehicles, & digital trade.
-
Export diversification will be key to balancing trade.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
In conclusion, Vietnam–Indonesia trade relations have evolved into a strategic economic partnership rooted in mutual dependence and long-term growth potential. Vietnam’s imports from Indonesia, led by coal, steel, vehicles, and industrial inputs, are fundamental to its industrialization and export success.
While Vietnam continues to run a trade deficit, the nature of its imports supports productive capacity rather than consumption alone. With strong policy frameworks, complementary economic structures, & ambitious growth targets, Vietnam–Indonesia trade is set to deepen further through 2025 and beyond, reinforcing ASEAN’s role as one of the world’s most dynamic economic regions.
For more insights into the latest Vietnam export-import data, or to search live data on Vietnam imports by country, visit VietnamExportdata. Contact us at info@tradeimex.in for customized Vietnam trade reports & market insights.
Share
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0