Exploring the Data on Vietnam Trade Partners in 2025: Vietnam's Biggest Trade Partners & Key Insights
Explore Vietnam’s top trade partners in 2025 with import-export data, top countries, sector-wise dependencies, and key insights shaping Vietnam's trade.

Vietnam’s rise as a global trading nation has been one of the most significant economic stories of the past two decades. In 2025, Vietnam stands firmly among the world’s most trade-dependent and export-driven economies, leveraging its strategic location, competitive labor force, and extensive network of free trade agreements. According to the latest Vietnam import data, the total value of Vietnam imports reached around $455.01 billion in 2025, a 19.4% increase from the previous year. According to the Vietnam export data, Vietnam exports accounted for $475.04 billion in 2025, an increase of 17% from the previous year. As global supply chains continue to realign in response to geopolitical tensions, rising production costs, and diversification strategies, Vietnam has emerged as a critical beneficiary.
Vietnam is one of the fastest-growing economies in the world and is among the top 15 largest trading countries, as per the Vietnam customs data and global trade data. This blog takes a deep, data-driven look at Vietnam’s trade partners in 2025, examining total trade values, leading export and import partners, sector-wise dependencies, and the strategic insights shaping Vietnam’s position in global trade.
Vietnam’s Trade Overview in 2025
In 2025, Vietnam’s total trade turnover (exports + imports) reached USD 930.05 billion, reinforcing its status as one of the most open economies globally. Trade value represents more than 170% of Vietnam’s GDP, highlighting the country’s heavy reliance on international commerce.
-
Total Exports (2025): $475.04 billion
-
Total Imports (2025): $455.01 billion
-
Trade Balance: Moderate surplus of USD 20 billion
Despite global economic uncertainty and slower demand growth in major markets, Vietnam maintained steady trade momentum, supported by electronics exports, machinery, textiles, and agricultural goods.
Why Vietnam’s Trade Partner Structure Matters
Vietnam’s trade partner mix provides insight into:
-
Global supply chain realignment
-
Dependence on foreign inputs for manufacturing
-
Exposure to geopolitical and tariff risks
-
Long-term industrial competitiveness
Unlike resource-based exporters, Vietnam operates primarily as a manufacturing and assembly hub, meaning its imports and exports are tightly interconnected, as per the Trade Statistics of Vietnam Customs.
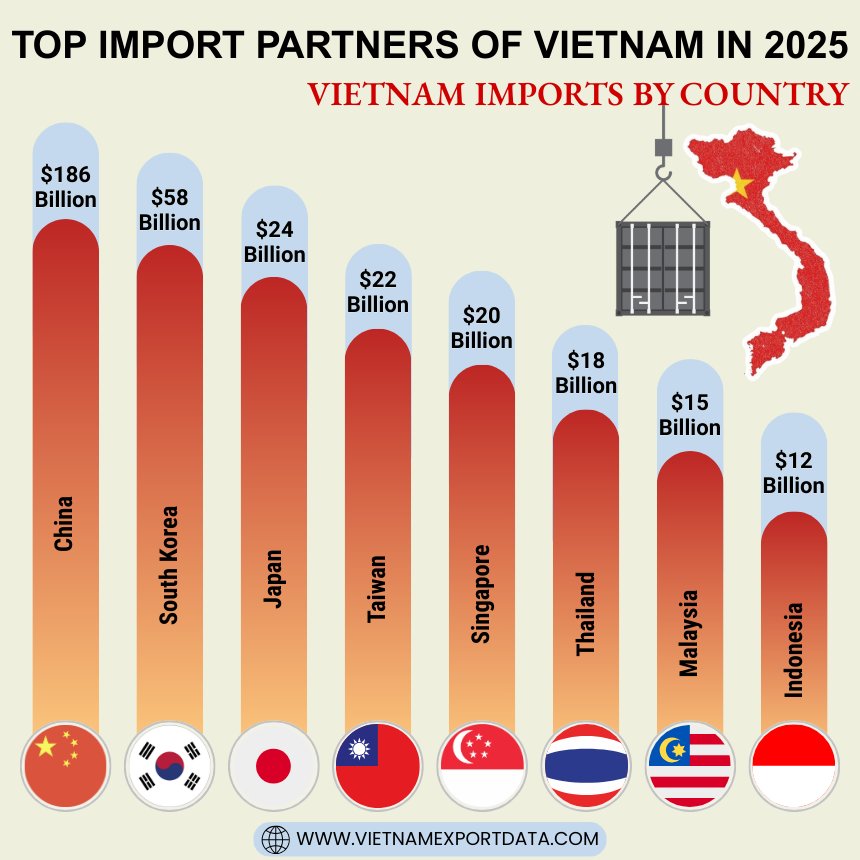
Top Import Partners of Vietnam in 2025: Vietnam Imports by Country
Vietnam's top import partners play a crucial role in shaping the country's trade landscape. Among the prominent import partners of Vietnam are China, South Korea, Japan, and the United States. China stands out as one of the most significant contributors to Vietnam's imports, followed closely by South Korea and Japan. The United States also holds a substantial position as an import partner for Vietnam. These countries not only facilitate the inflow of goods into Vietnam but also contribute to the country's economic growth through trade partnerships. The top trade partners of Vietnam for imports, as per the Vietnam shipment data for 2025, include:
1. China: USD 186 Billion (39.6%)
China overwhelmingly dominated Vietnam’s import structure in 2025, supplying nearly two-fifths of all imports, as per the data on Vietnam imports from China by HS code.
Major imports:
-
Electronic components and semiconductors
-
Machinery and production equipment
-
Textile fabrics and accessories
-
Chemicals, plastics, and steel
Vietnam’s electronics, textiles, and machinery exports remain heavily dependent on Chinese upstream inputs.
2. South Korea: USD 58 Billion (12.3%)
South Korea ranked second, driven by strong FDI-led supply chains, especially in electronics.
Major imports:
-
Semiconductor chips
-
Display panels
-
Precision machinery
-
Industrial chemicals
Samsung and other Korean conglomerates anchor this trade flow.
3. Japan: USD 24 Billion (5.1%)
Japan remained a key supplier of high-value capital goods.
Major imports:
-
Industrial and factory machinery
-
Automotive components
-
Electrical and robotic equipment
Japanese imports support Vietnam’s move toward advanced manufacturing.
4. Taiwan: USD 22 Billion (4.7%)
Taiwan played a critical role in Vietnam’s electronics ecosystem.
Major imports:
-
Printed circuit boards
-
Semiconductor parts
-
Precision electronic components
Taiwanese suppliers are essential to Vietnam’s export-oriented electronics sector.
5. Singapore: USD 20 Billion (4.3%)
Singapore functioned largely as a regional trading and re-export hub.
Major imports:
-
Refined petroleum products
-
Chemicals
-
Electronics and machinery re-exports
Many goods routed via Singapore originated in third countries.
6. Thailand: USD 18 Billion (3.8%)
Thailand’s position reflects deep ASEAN supply chain integration.
Major imports:
-
Automotive parts
-
Petrochemicals
-
Plastics and resins
-
Processed food inputs
7. Malaysia: USD 15 Billion (3.2%)
Malaysia supplied both energy and electronics-related inputs.
Major imports:
-
LNG and petroleum products
-
Semiconductor components
-
Electrical machinery
8. Indonesia: USD 12 Billion (2.6%)
Indonesia’s exports to Vietnam were largely resource-based.
Major imports:
-
Coal
-
Petroleum products
-
Palm oil
-
Basic industrial materials
These imports support power generation and food processing.
9. United States: USD 11 Billion (2.3%)
While the US is Vietnam’s top export destination, it plays a smaller role as an import supplier.
Major imports:
-
Aircraft and aerospace parts
-
Agricultural commodities (soybeans, cotton)
-
High-tech machinery
US imports are lower in volume but higher in unit value.
10. Germany: USD 9 Billion (1.9%)
Germany remained Vietnam’s leading European import partner.
Major imports:
-
Industrial machinery
-
Automotive systems
-
Electrical equipment
-
Specialty chemicals
Summary: Vietnam’s Top 10 Import Partners (2025)
|
Rank |
Country |
Import Value ($) |
Share of Total Imports |
|
1 |
China |
$186 Billion |
39.6% |
|
2 |
South Korea |
$58 Billion |
12.3% |
|
3 |
Japan |
$24 Billion |
5.1% |
|
4 |
Taiwan |
$22 Billion |
4.7% |
|
5 |
Singapore |
$20 Billion |
4.3% |
|
6 |
Thailand |
$18 Billion |
3.8% |
|
7 |
Malaysia |
$15 Billion |
3.2% |
|
8 |
Indonesia |
$12 Billion |
2.6% |
|
9 |
United States |
$11 Billion |
2.3% |
|
10 |
Germany |
$9 Billion |
1.9% |
Key Insights from the Share Distribution
-
China alone supplies nearly 40% of Vietnam’s imports, highlighting high upstream dependency.
-
East Asia (China, Korea, Japan, Taiwan) accounts for over 61% of total imports.
-
ASEAN partners contribute stability and regional resilience.
-
Western suppliers (US, Germany) focus on high-value, specialized goods rather than volume.
-
Vietnam’s import structure clearly reflects its role as a manufacturing and assembly hub within global value chains.
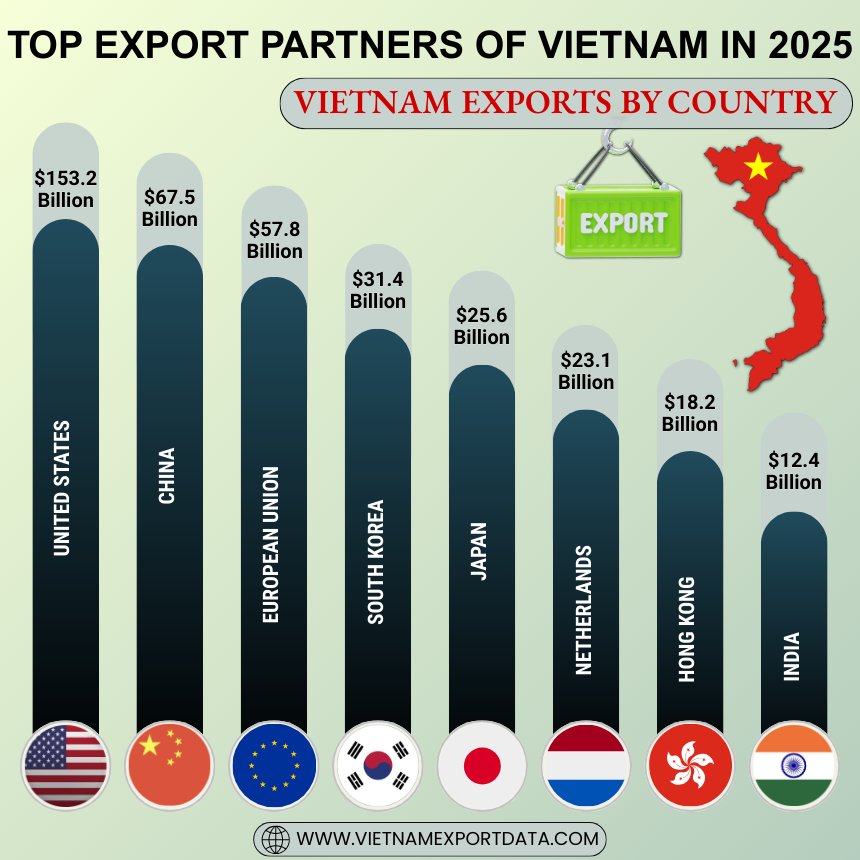
Top Export Partners of Vietnam in 2025: Vietnam Exports by Country
Vietnam's top export partners play a crucial role in shaping its export landscape. The prominent export destinations for Vietnam include countries like the United States, China, Japan, South Korea, and Germany. These alliances contribute significantly to Vietnam's economic growth through trade partnerships in various sectors such as electronics, textiles, and agriculture. Vietnam's top 10 export partners or trade partners for exports, as per Vietnam trade data for 2025, include:
1. United States: USD 153.2 Billion (37.4%)
The United States remained Vietnam’s largest export market by a wide margin, absorbing more than one-third of total exports, as per the data on Vietnam exports to the US by HS code.
Key exports:
-
Electronics and smartphones
-
Computers and electrical equipment
-
Apparel, footwear, and textiles
-
Furniture and wood products
-
Machinery and mechanical appliances
Vietnam’s export relationship with the US is demand-driven, consumer-focused, and central to its trade surplus.
2. China: USD 67.5 Billion (16.5%)
China ranked second as an export destination, playing a dual role as both a major buyer and supplier.
Key exports:
-
Electronics and components
-
Agricultural products (fruits, rubber, seafood)
-
Machinery and intermediate goods
Exports to China are closely tied to regional production networks and cross-border supply chains.
3. European Union (EU): USD 57.8 Billion (14.1%)
The EU collectively remained Vietnam’s third-largest export partner.
Key exports:
-
Apparel and textiles
-
Footwear
-
Furniture
-
Consumer electronics
Preferential access under free trade agreements has helped Vietnam expand market share across Europe.
4. South Korea: USD 31.4 Billion (7.7%)
South Korea’s position reflects strong intra-firm and FDI-linked trade.
Key exports:
-
Electronic components
-
Machinery
-
Textiles
-
Processed industrial goods
Much of this trade supports Korean manufacturers operating in Vietnam.
5. Japan: USD 25.6 Billion (6.2%)
Japan remained a stable, high-value export destination.
Key exports:
-
Machinery and equipment
-
Electronics
-
Textiles and garments
-
Seafood and agricultural products
Japan’s emphasis on quality standards has encouraged Vietnam’s move up the value chain.
6. Netherlands: USD 23.1 Billion (5.6%)
Vietnam-Netherlands trade continued to grow steadily.
Key exports:
-
Electronics
-
Petroleum products
-
Food and agricultural goods
-
Construction materials
Geographic proximity and tariff preferences supported regional trade flows.
7. Hong Kong: USD 18.2 Billion (4.4%)
Hong Kong functioned primarily as a re-export and trade hub.
Key exports:
-
Electronics and components
-
High-value consumer goods
A significant portion of exports routed through Hong Kong were destined for third markets.
8. India: USD 12.4 Billion (3%)
India emerged as a growing export destination for Vietnam in South Asia.
Key exports:
-
Electronics
-
Machinery
-
Chemicals
-
Agricultural products
Trade diversification strategies helped strengthen Vietnam–India trade ties.
9. Australia: USD 11.3 Billion (2.8%)
Australia remained a reliable market for both industrial and consumer goods.
Key exports:
-
Electronics
-
Textiles and garments
-
Seafood and food products
10. Canada: USD 10.3 Billion (2.5%)
Canada completed the top 10, supported by CPTPP-related trade facilitation.
Key exports:
-
Apparel and footwear
-
Furniture
-
Consumer electronics
Summary: Vietnam’s Top 10 Export Partners (2025)
|
Rank |
Country |
Export Value ($) |
Share of Total Exports |
|
1 |
United States |
153.2 Billion |
37.4% |
|
2 |
China |
67.5 Billion |
16.5% |
|
3 |
European Union |
57.8 Billion |
14.1% |
|
4 |
South Korea |
31.4 Billion |
7.7% |
|
5 |
Japan |
25.6 Billion |
6.2% |
|
6 |
Netherlands |
23.1 Billion |
5.6% |
|
7 |
Hong Kong |
18.2 Billion |
4.4% |
|
8 |
India |
12.4 Billion |
3.0% |
|
9 |
Australia |
11.3 Billion |
2.8% |
|
10 |
Canada |
10.3 Billion |
2.5% |
Key Insights from Vietnam’s Export Partner Shares (2025)
-
The US alone absorbed nearly 38% of Vietnam’s exports, making it Vietnam’s most critical demand market.
-
China and the EU together accounted for over 30%, highlighting balanced exposure between Asia and the West.
-
FDI-driven trade with South Korea and Japan remains structurally important.
-
ASEAN & CPTPP markets support diversification but remain secondary in scale.
-
Vietnam’s export profile is highly concentrated, creating both efficiency and policy risk.
Sector-Wise Trade Dependency
Electronics and Electrical Equipment
Electronics account for over 35% of Vietnam’s total exports.
-
Heavy import dependence on China and South Korea
-
Major export markets: US, EU, China
This sector defines Vietnam’s trade structure.
Textiles and Apparel
Textiles remain a cornerstone export sector.
-
Exports exceed USD 40 billion
-
Heavy reliance on imported fabrics from China, South Korea, and Taiwan
Vietnam’s ability to comply with free trade agreement rules of origin remains a strategic challenge.
Machinery and Mechanical Appliances
-
Exports: USD 45+ billion
-
Imports: USD 60+ billion
This reflects Vietnam’s role in assembling machinery and exporting finished or semi-finished products.
Agriculture and Seafood
Agricultural exports contribute around USD 55 billion.
-
Key markets: China, US, Japan, EU
-
Vietnam is among the world’s top exporters of rice, coffee, seafood, and fruits
Trade Agreements and Their Impact on Partner Dynamics
Vietnam is party to more than 15 free trade agreements, including:
-
CPTPP
-
RCEP
-
EU-Vietnam FTA
-
ASEAN FTAs
These agreements have:
-
Reduced tariff barriers
-
Increased export diversification
-
Encouraged foreign investment
They also influence which partners gain or lose trade share over time.
Key Trade Insights from Vietnam’s 2025 Data
1. High Import Concentration Risk
Vietnam’s heavy reliance on China and South Korea for imports exposes it to supply chain risks and cost volatility.
2. Strong Export Market Concentration
Nearly 45% of exports go to the US and China combined, making Vietnam sensitive to policy changes in these economies.
3. Rising Value Addition
Exports are shifting gradually from low-value assembly toward higher-value electronics and machinery.
4. Strategic Role in “China+1” Strategy
Vietnam remains the biggest beneficiary of supply chain diversification away from China.
Challenges Facing Vietnam’s Trade Model
Despite its success, Vietnam faces structural challenges:
-
Limited domestic supply of key components
-
Infrastructure bottlenecks at ports and trade hubs
-
Rising labor and land costs
-
Increasing scrutiny from trade partners on origin and compliance
Addressing these issues is critical for sustaining growth.
Outlook: Vietnam’s Trade Partners Beyond 2025
Looking ahead:
-
Trade with the US and EU will remain demand-driven
-
Regional Asian integration will deepen under RCEP
-
India, the Middle East, and Africa may emerge as new growth markets
-
Domestic supplier development will become a policy priority
Vietnam is expected to maintain trade growth of 6–7% annually over the next decade.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
In conclusion, in 2025, Vietnam stands at the center of global trade realignment. Its biggest trade partners, China, the United States, South Korea, the European Union, and Japan, reflect a balanced mix of supply-side and demand-side relationships.
Vietnam’s trade data reveals a country that has successfully positioned itself as a global manufacturing hub, while still facing challenges related to dependency, concentration, and value addition. For businesses, policymakers, & investors, understanding Vietnam’s trade partner dynamics is essential for navigating Asia’s evolving economic landscape. Vietnam’s story in 2025 is not just about growth. It is about strategic integration into the global economy, and the data makes that clear.
For more insights into the latest Vietnam trade data, or to search live Vietnam import-export data by country, visit VietnamExportdata. Contact us at info@tradeimex.in for customized trade reports & market insights.
Share
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0