Latest Machinery Import Data of Vietnam: Vietnam’s Dependence on Imported Machinery & Industrial Equipment
Explore Vietnam’s latest machinery import data, top supplier countries, key trends, & why Vietnam remains dependent on imported machinery.
Vietnam’s rise as a regional manufacturing powerhouse is one of the most significant economic stories in Asia over the last two decades. From electronics and textiles to automotive assembly and heavy industry, Vietnam has steadily positioned itself as a preferred destination for global production. At the heart of this transformation lies one critical factor: imported machinery and industrial equipment. According to the latest Vietnam import data and Vietnam customs import data of machinery, the total value of Vietnam machinery imports reached $28.46 billion in 2024-25, a 22% increase from the previous year. Vietnam imported machinery worth $33.49 billion in 2025.
Vietnam is the 29th-largest machinery importer in the world, according to global trade data. Nuclear reactors & machinery constitute 7.51% of Vietnam's total imports, as per Vietnam Customs data. Despite strong growth in domestic manufacturing output, Vietnam remains highly dependent on foreign machinery, equipment, and industrial technology. This dependence is reflected clearly in the country’s import statistics, industrial structure, and investment patterns. This blog takes a deep, data-driven look at Vietnam’s latest machinery import data, the reasons behind its reliance on imports, and the broader implications for its economy and industrial future.
Vietnam’s Machinery Imports at a Glance
Machinery and industrial equipment consistently rank among Vietnam’s largest import categories, alongside electronics components and raw materials for manufacturing. In 2024, Vietnam’s total merchandise imports were valued at approximately USD 380–385 billion. Of this figure:
-
Machinery, equipment, tools, & spare parts accounted for nearly USD 49 billion.
-
This category represented around 13% of total imports
-
Machinery imports grew by over 17% year-on-year, signaling renewed industrial expansion after global supply chain disruptions in earlier years
When combined with electronics, machinery, and electrical equipment used in production, machinery-related imports form the backbone of Vietnam’s industrial supply chain.
This level of import activity is not incidental. It directly reflects Vietnam’s machinery imports & economic model, which is centered on:
-
Export-oriented manufacturing
-
Foreign direct investment (FDI)
-
Integration into global production networks
Vietnam Machinery Imports by Country: Where Does Vietnam Import Machinery?
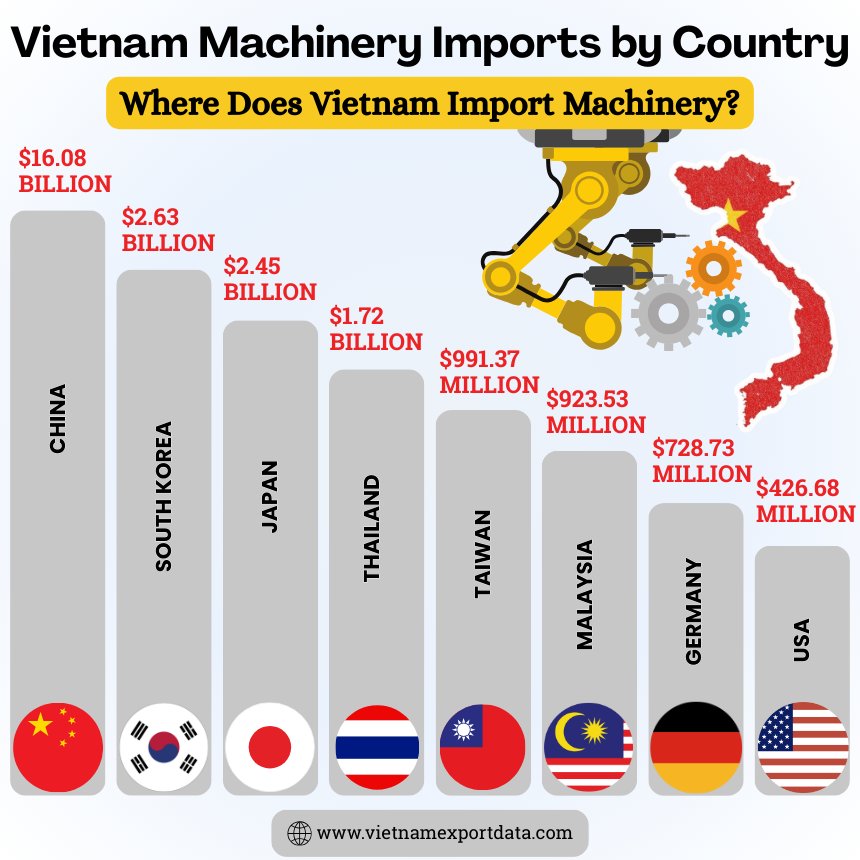
In recent years, Vietnam has seen a significant increase in its imports of machinery, with a growing demand for machinery & equipment across various sectors of the economy. Vietnam's machinery imports come from various countries around the globe, reflecting the country's diverse trade relationships. Mainly, Vietnam imports machinery from China, South Korea, and Japan. These countries are significant sources of advanced technology and machinery that support Vietnam's industrial and manufacturing sectors. The top 10 machinery supplier countries to Vietnam, as per the Vietnam shipment data for 2025, include:
1. China: $16.08 billion (56.5%)
Unsurprisingly, China emerges as the top country from which Vietnam imports machinery, accounting for a substantial 56.5% of all machinery imports, as per the data on Vietnam machinery imports from China by HS code. China has long been a major trading partner for Vietnam, with a wide range of machinery and equipment being imported to support various industries in the country.
2. South Korea: $2.63 billion (9.3%)
South Korea is another significant player in Vietnam's machinery import market, contributing 9.3% of the total machinery imports. South Korean machinery is known for its quality and innovation, making it a popular choice for Vietnamese businesses looking to invest in new equipment.
3. Japan: $2.45 billion (8.6%)
Japan is a key player in the global machinery market, and Vietnam is no exception. With 8.6% of the total machinery imports coming from Japan, it's clear that Vietnamese businesses value the high-quality machinery and advanced technology that Japan has to offer, as per the data on Vietnam machinery imports from Japan.
4. Thailand: $1.72 billion (6.1%)
Thailand is another important source of machinery imports for Vietnam, accounting for 6.1% of the total machinery imports. With a focus on machinery for agriculture, electronics, and automotive industries, Thailand offers a diverse range of machinery options for Vietnamese businesses.
5. Taiwan: $991.37 million (3.5%)
Taiwan is known for its expertise in manufacturing machinery and equipment, and Vietnamese businesses are taking advantage of this by importing $991.37 million worth of machinery from Taiwan. With a focus on precision machinery and electronics, Taiwan is a valuable partner for Vietnam's machinery needs.
6. Malaysia: $923.53 million (3.2%)
Malaysia is another important player in Vietnam's machinery import market, contributing 3.2% of the total machinery imports. With a focus on machinery for the construction, manufacturing, and electronics industries, Malaysian machinery is a popular choice for Vietnamese businesses.
7. Germany: $728.73 million (2.6%)
German machinery is synonymous with quality and precision, and Vietnamese businesses are willing to pay a premium for it. With $728.73 million worth of machinery imports coming from Germany, it's clear that Vietnamese businesses value the reliability and innovation that German machinery offers.
8. USA: $426.68 million (1.5%)
The United States may not be the largest source of machinery imports for Vietnam, but it still plays a significant role in the market. With $426.68 million worth of machinery imports, the USA supplies a range of machinery and equipment to support various industries in Vietnam.
9. India: $364.38 million (1.3%)
India is emerging as an important player in Vietnam's machinery import market, with $364.38 million worth of machinery imports. With a focus on machinery for the textile, automotive, and electronics industries, Indian machinery offers affordable and reliable options for Vietnamese businesses.
10. Italy: $327.95 million (1.2%)
Italy may be a smaller player in Vietnam's machinery import market, but it still offers valuable machinery options for Vietnamese businesses. With $327.95 million worth of machinery imports, Italian machinery is known for its quality and design, making it a popular choice for certain industries in Vietnam.
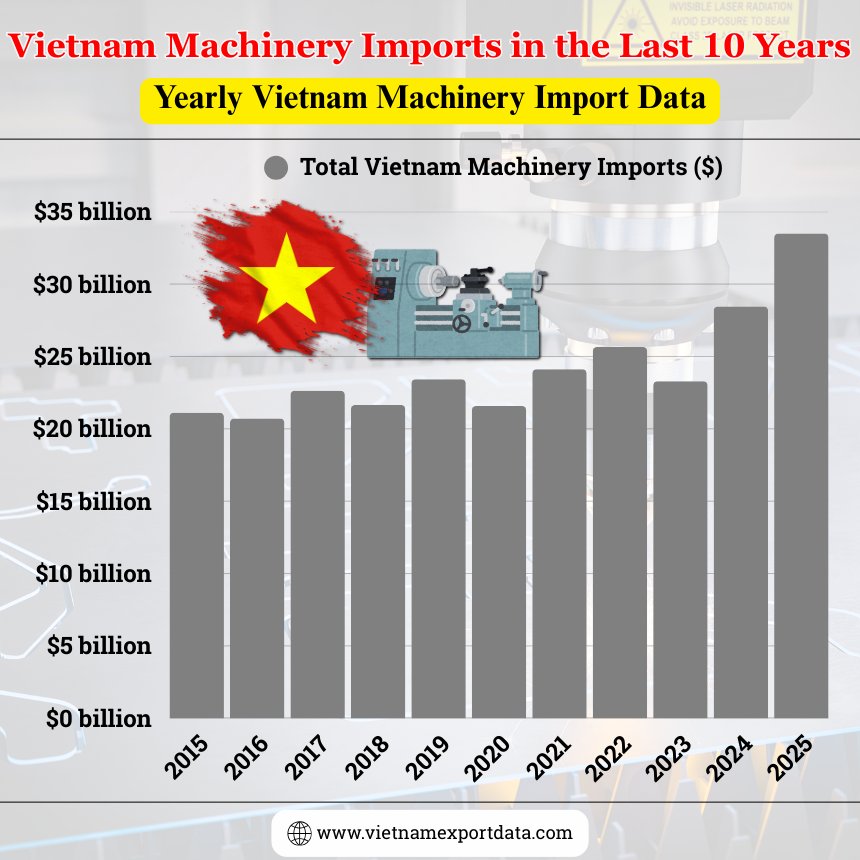
Vietnam Machinery Imports in the Last 10 Years: Yearly Vietnam Machinery Import Data
|
Year of Trade |
Total Vietnam Machinery Imports ($) |
|
2015 |
$21.11 billion |
|
2016 |
$20.72 billion |
|
2017 |
$22.63 billion |
|
2018 |
$21.65 billion |
|
2019 |
$23.43 billion |
|
2020 |
$21.57 billion |
|
2021 |
$24.11 billion |
|
2022 |
$25.65 billion |
|
2023 |
$23.29 billion |
|
2024 |
$28.46 billion |
|
2025 |
$33.49 billion |
Key Categories of Machinery Imported by Vietnam
Vietnam imports a wide range of industrial machinery, from heavy equipment used in infrastructure and manufacturing to precision tools used in electronics assembly.
1. Industrial Production Machinery
A significant share of imports consists of general industrial machinery, including:
-
CNC machines
-
Metal-cutting and metal-forming machines
-
Injection molding machines for plastics and rubber
-
Industrial presses and stamping machines
-
Textile and garment manufacturing machinery
These machines are widely used in:
-
Automotive assembly
-
Electronics manufacturing
-
Textile and apparel production
-
Consumer goods manufacturing
Vietnam’s domestic production of such machinery remains limited in both scale and technological sophistication, making imports essential.
2. Electronics and Semiconductor Manufacturing Equipment
One of the fastest-growing machinery import segments is electronics manufacturing equipment. This includes:
-
PCB assembly machines
-
Chip testing and inspection equipment
-
Automated pick-and-place machines
-
Optical readers and scanning systems
-
Clean-room machinery and precision handling tools
In 2024 alone:
-
Imports of computer-related machinery and accessories exceeded USD 4.5 billion.
-
Imports of computers, optical readers, and automated data processing machines reached USD 2.4 billion.
This growth is driven by Vietnam’s expanding role in global electronics supply chains, serving multinational manufacturers producing smartphones, computers, and consumer electronics.
3. Mechanical Equipment and Industrial Components
Vietnam also imports large volumes of mechanical components and auxiliary equipment, such as:
-
Pumps, compressors, and vacuum systems
-
Valves, taps, and flow control devices
-
Bearings, gears, and transmission components
-
Lifting and material handling machinery
-
Industrial refrigeration and HVAC systems
These imports are essential for:
-
Factory operations
-
Power generation
-
Oil, gas, and energy infrastructure
-
Construction and logistics facilities
In many cases, these components must meet international technical standards, making domestic alternatives insufficient or unavailable.
4. Heavy Machinery and Specialized Equipment
Specialized and capital-intensive machinery imports include:
-
Turbo-jets and gas turbines
-
Power generation equipment
-
Mining and quarrying machinery
-
Construction machinery for large infrastructure projects
While these imports fluctuate year to year depending on investment cycles, they remain strategically important for Vietnam’s long-term industrialization.
Why Vietnam Depends on Imported Machinery
Vietnam’s heavy reliance on imported machinery is structural rather than temporary. Several underlying factors explain this dependence.
1. Limited Domestic Machinery Manufacturing Capacity
Despite rapid industrial growth, Vietnam’s domestic machinery manufacturing sector remains underdeveloped.
Estimates suggest that:
-
Over 70% of machinery and industrial equipment used in Vietnam is imported.
-
Domestic manufacturers focus mainly on simple machines, spare parts, and basic fabrication.
-
High-precision, automated, and capital-intensive machinery is largely unavailable locally.
This gap forces manufacturers to rely on imports to meet production requirements.
2. Export-Oriented Manufacturing Model
Vietnam’s economy is deeply export-driven. Key export sectors such as:
-
Electronics
-
Apparel and footwear
-
Furniture
-
Automotive components
All require globally standardized machinery to meet international quality, efficiency, and compliance standards.
Multinational companies operating in Vietnam often:
-
Specify machinery suppliers globally
-
Import production lines identical to those used in other countries
-
Avoid local machinery due to compatibility and quality concerns
As a result, machinery imports rise in tandem with export growth.
3. Foreign Direct Investment and Technology Transfer Patterns
FDI plays a dominant role in Vietnam’s industrial development. Foreign-invested enterprises account for:
-
A large share of industrial output
-
The majority of high-tech manufacturing
-
A significant portion of machinery imports
These firms typically import:
-
Complete production lines
-
Specialized tools
-
Proprietary equipment not produced locally
While FDI contributes to employment and exports, it also reinforces dependence on imported machinery.
4. Skills and Technology Constraints
Advanced machinery requires:
-
Skilled operators
-
Technical maintenance capabilities
-
Engineering expertise
Vietnam faces persistent challenges in:
-
High-skill labor availability
-
Industrial R&D capacity
-
Machine design and systems engineering
Without a strong ecosystem of engineers and machine builders, domestic machinery production remains limited.
Recent Trends in Vietnam’s Machinery Import Data
Post-Pandemic Rebound
After disruptions in global trade and investment, machinery imports rebounded strongly in 2023 and 2024.
Key drivers included:
-
Resumption of delayed investment projects
-
Expansion of electronics manufacturing
-
Infrastructure and construction activity
-
Automation upgrades to offset labor shortages
The double-digit growth in machinery imports reflects renewed confidence in Vietnam’s industrial outlook.
Shift Toward Automation and Smart Manufacturing
There is a visible shift in import composition toward:
-
Automated production lines
-
Robotics
-
Smart sensors and control systems
-
Energy-efficient machinery
This trend aligns with Vietnam’s push toward higher productivity and value-added manufacturing.
Concentration Risk in Supply Chains
Despite diversification efforts, machinery imports remain heavily concentrated among a few suppliers, particularly China.
This creates exposure to:
-
Geopolitical risks
-
Trade policy changes
-
Supply disruptions
-
Currency fluctuations
Managing this risk is becoming a growing concern for both policymakers and manufacturers.
Economic Implications of Machinery Import Dependence
Positive Impacts
Imported machinery has played a crucial role in:
-
Boosting manufacturing productivity
-
Supporting export competitiveness
-
Attracting foreign investment
-
Accelerating industrial modernization
Without access to foreign machinery, Vietnam’s rapid industrial growth would not have been possible.
Structural Challenges
At the same time, heavy import dependence creates challenges:
-
Large outflows of foreign currency
-
Limited development of domestic machinery industries
-
Vulnerability to external shocks
-
Persistent technology gaps
Even as Vietnam runs trade surpluses overall, machinery imports represent a major cost within the production system.
Policy and Strategic Outlook
Vietnam has recognized the need to:
-
Develop supporting industries
-
Encourage domestic machinery production
-
Improve workforce skills
-
Promote technology transfer
However, building a competitive domestic machinery sector is a long-term endeavor that requires:
-
Substantial capital investment
-
Strong industrial policy coordination
-
Collaboration between government, universities, and industry
In the near to medium term, Vietnam is likely to remain dependent on imported machinery, especially in high-tech and capital-intensive sectors.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
In conclusion, Vietnam’s latest machinery import data clearly shows that Vietnam’s industrial growth is deeply intertwined with imported machinery and industrial equipment. With imports nearing USD 49 billion annually, machinery is not just another trade category; it is the foundation of Vietnam’s manufacturing economy.
Key takeaways:
-
Vietnam imports the majority of its industrial machinery
-
China, South Korea, and Japan dominate the supply
-
Import dependence is driven by export-oriented manufacturing, FDI, and limited domestic capacity
-
While imports support growth, they also create structural vulnerabilities
As Vietnam continues its transition toward higher-value manufacturing, the challenge will be to balance openness to global technology with the gradual development of domestic industrial capabilities. Until then, imported machinery will remain a defining feature of Vietnam’s economic landscape.
For more insights into the latest Vietnam export-import data, or to search live data on Vietnam machinery imports by country, visit VietnamExportdata. Contact us at info@tradeimex.in for customized trade reports, market insights, and a verified database of the top machinery importers in Vietnam.
Share
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0















