Vietnam-Japan Trade Relations 2025: Top Traded Products & JVEPA Insights
Explore Vietnam–Japan trade relations in 2025, including top traded products, bilateral trade trends, & how VJEPA shapes trade & future opportunities.

Introduction: A Mature and Strategic Trade Partnership
By 2025, Vietnam–Japan trade relations have reached a level of maturity that few bilateral partnerships in Asia can match. What began decades ago as a development-oriented relationship has evolved into a deeply integrated economic partnership spanning trade in goods, investment, technology transfer, industrial cooperation, and supply-chain resilience. According to the latest Vietnam import data and Japan export data, the total value of Vietnam imports from Japan reached $21.44 billion in 2024. Meanwhile, the total value of Vietnam exports to Japan reached $24.55 billion in 2024, according to the Vietnam export data. The total Vietnam-Japan trade accounted for $46 billion in 2024-25.
Japan is the 4th largest trading partner of Vietnam, as per the latest global trade data and Vietnam customs data. Japan remains one of Vietnam’s most important economic partners, while Vietnam has emerged as one of Japan’s most dynamic production and sourcing hubs in Southeast Asia. The relationship is underpinned by strong political trust, long-term Japanese investment in Vietnam’s industrial base, and a network of trade agreements, with the Vietnam–Japan Economic Partnership Agreement (VJEPA) playing a central role.
Using 2024 trade data as the most recent full-year reference point, this report examines:
-
Overall trade performance and structure
-
Top traded products by category and value
-
Sector-level dynamics shaping exports and imports
-
How VJEPA continues to influence trade outcomes
-
Key challenges and opportunities moving into 2025 and beyond
Overview of Vietnam–Japan Trade
Total Trade Value and Balance
In 2024, total bilateral trade between Vietnam and Japan reached approximately USD 46–47 billion, consolidating Japan’s position as one of Vietnam’s top five trading partners. In the first 7 months of 2025, the total Vietnam-Japan trade value reached $28.7 billion.
-
Vietnam’s exports to Japan: USD 24.5 billion
-
Japan’s exports to Vietnam: USD 17.1 billion
-
Vietnam’s trade surplus: USD 9.5 billion
Vietnam has consistently maintained a trade surplus with Japan over the past decade. This reflects:
-
Vietnam’s strength in labor-intensive manufacturing and consumer goods
-
Japan’s role as a supplier of capital goods rather than final consumer products
Structural Characteristics of Trade
Vietnam–Japan trade is notable for its high degree of complementarity:
-
Vietnam exports finished or semi-finished goods such as electronics assemblies, apparel, furniture, footwear, and food products.
-
Japan exports machinery, equipment, materials, and advanced components that feed directly into Vietnam’s production systems.
This structure reduces direct competition and supports long-term stability in bilateral trade.
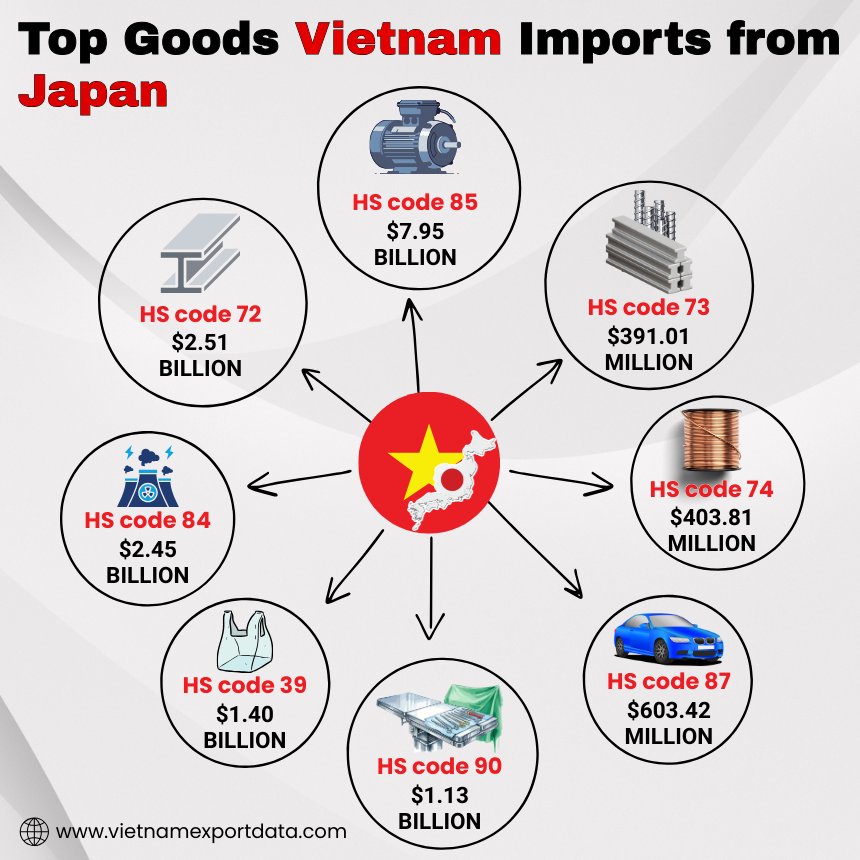
Top Goods Vietnam Imports from Japan: What Does Vietnam Import from Japan?
Vietnam has established a strong trading relationship with Japan, importing a variety of top goods to meet its economic needs. Among the top goods Vietnam imports from Japan are machinery, electronics, and vehicles. These imports play a crucial role in supporting Vietnam's industrial & technological growth. The top 10 goods that Vietnam imports from Japan, as per the Vietnam-Japan trade data & Vietnam shipment data for 2024-25, include:
1. Electrical machinery & equipment (HS code 85): $7.95 billion
One of the top goods that Vietnam imports from Japan is electrical machinery and equipment, with a total value of $7.95 billion. This includes items such as electronics, appliances, and other electrical components that are essential for various industries in Vietnam.
2. Iron & steel (HS code 72): $2.51 billion
Iron and steel products are also among the top goods that Vietnam imports from Japan, with a total value of $2.51 billion. These materials are crucial for construction, manufacturing, and infrastructure development in Vietnam.
3. Nuclear reactors & machinery (HS code 84): $2.45 billion
Nuclear reactors and machinery are another significant import from Japan to Vietnam, with a total value of $2.45 billion, as per the data on Vietnam machinery imports from Japan by HS code. These items play a vital role in energy production and industrial processes in Vietnam.
4. Plastics & articles thereof (HS code 39): $1.40 billion
Plastics and plastic articles are also high on the list of goods that Vietnam imports from Japan, with a total value of $1.40 billion. These products are widely used in various sectors, including packaging, construction, and automotive industries.
5. Optical, medical, & surgical instruments (HS code 90): $1.13 billion
Optical, medical, and surgical instruments are essential imports for Vietnam, with a total value of $1.13 billion. These items are critical for the healthcare sector, research institutions, and scientific laboratories in Vietnam.
6. Vehicles (HS code 87): $603.42 million
Japan is known for its high-quality vehicles, and Vietnam imports a significant number of cars, trucks, and other vehicles from Japan, with a total value of $603.42 million. Japanese automakers have a strong presence in the Vietnamese market.
7. Copper & articles thereof (HS code 74): $403.81 million
Copper and copper articles are also among the top imports from Japan to Vietnam, with a total value of $403.81 million. These materials are crucial for electrical wiring, plumbing, and other applications in Vietnam.
8. Articles of iron or steel (HS code 73): $391.01 million
Besides raw iron and steel, Vietnam also imports articles made of iron or steel from Japan, with a total value of $391.01 million. These products are utilised in various industries, including construction, machinery, and the automotive sector.
9. Rubber & articles thereof (HS code 40): $335.18 million
Rubber and rubber articles are important imports for Vietnam, with a total value of $335.18 million, as per the data on Vietnam rubber imports from Japan. These items are crucial for the production of tyres, seals, and other rubber products in Vietnam.
10. Man-made filaments (HS code 54): $306.55 million
Lastly, man-made filaments are among the top imports from Japan to Vietnam, with a total value of $306.55 million. These materials are used in the textile, automotive, and construction industries in Vietnam.
Top Products Vietnam Exports to Japan: What Does Vietnam Export to Japan?
Vietnam has become a key player in the export market to Japan, with a variety of top products demonstrating its strength in the economic landscape. Among the leading exports to Japan from Vietnam are electronics, textiles, agricultural goods, and seafood. These products showcase Vietnam's diverse range of industries and its ability to meet the demands of the Japanese market. The top 10 products that Vietnam exports to Japan, as per the Vietnam trade data for 2024-25, include:
1. Electrical Machinery & Equipment (HS code 85): $6.34 billion
Electrical machinery and equipment are among the top products that Vietnam exports to Japan, as per the data on Vietnam electronics exports to Japan by HS code. This category includes items such as electrical transformers, electric motors, and insulated wire, among others. With technological advancements driving the demand for such products, Vietnam has carved out a significant share in the Japanese market.
2. Articles of Apparel, Knitted (HS code 61): $2.13 billion
Vietnam is known for its thriving textile and garment industry, and this is reflected in its exports to Japan. Articles of apparel, especially knitted items like sweaters, t-shirts, and socks, are popular among Japanese consumers. Vietnam's competitive pricing and quality products have helped it become a key player in this segment.
3. Articles of Apparel, Not Knitted (HS code 62): $1.88 billion
Apart from knitted apparel, Vietnam also exports a significant amount of non-knitted apparel to Japan. This category includes items such as trousers, suits, and jackets. The country's skilled workforce and robust manufacturing capabilities have enabled it to meet the diverse needs of the Japanese market.
4. Nuclear Reactors & Machinery (HS code 84): $1.60 billion
Vietnam's exports of nuclear reactors and machinery to Japan play a crucial role in supporting the latter's energy infrastructure. As Japan seeks to diversify its energy mix and invest in cleaner technologies, Vietnam's contributions in this sector are highly valued. This underscores the strong economic ties between the two countries.
5. Wood & Articles of Wood (HS code 44): $1.32 billion
Wood and articles of wood constitute another major category of exports from Vietnam to Japan. This includes items such as furniture, plywood, and wooden frames. Japan's demand for high-quality wood products has created opportunities for Vietnamese exporters to showcase their craftsmanship and innovative designs.
6. Footwear (HS code 64): $1.11 billion
Vietnam's footwear industry has gained global recognition for its stylish designs and affordable pricing. Japanese consumers have a penchant for quality footwear, making Vietnam a preferred supplier in this segment. From sneakers to sandals, Vietnamese shoe manufacturers cater to a wide range of preferences in the Japanese market.
7. Fish & Seafood (HS code 03): $947.51 million
Vietnam's coastal geography and abundant marine resources make it a prime source of fish and seafood products for Japan. With a reputation for fresh and sustainably sourced products, Vietnamese exporters have established a strong foothold in the Japanese seafood market. From shrimp to fish fillets, Vietnam's seafood exports continue to grow steadily.
8. Plastics & Articles Thereof (HS code 39): $939.52 million
Plastics and articles made from plastic are among the top exports from Vietnam to Japan. This category encompasses a wide range of products, including plastic containers, packaging materials, and household items. With a focus on quality and durability, Vietnamese plastic manufacturers cater to the diverse needs of the Japanese market.
9. Furniture, Bedding, & Mattresses (HS code 94): $802.29 million
Vietnam's furniture industry is renowned for its artisanal craftsmanship and modern designs. The country's exports of furniture, bedding, and mattresses to Japan have gained popularity among Japanese consumers seeking stylish and functional home decor solutions. Vietnam's furniture exports continue to showcase its creativity and innovation in this competitive market.
10. Vehicles (HS code 87): $616.03 million
Vietnam's exports of vehicles, including automobiles and automotive parts, have increased in recent years. Japanese automakers have established manufacturing plants in Vietnam, creating a symbiotic trade relationship between the two countries. Vietnam's exports of vehicles to Japan reflect the country's growing capabilities in the automotive sector.
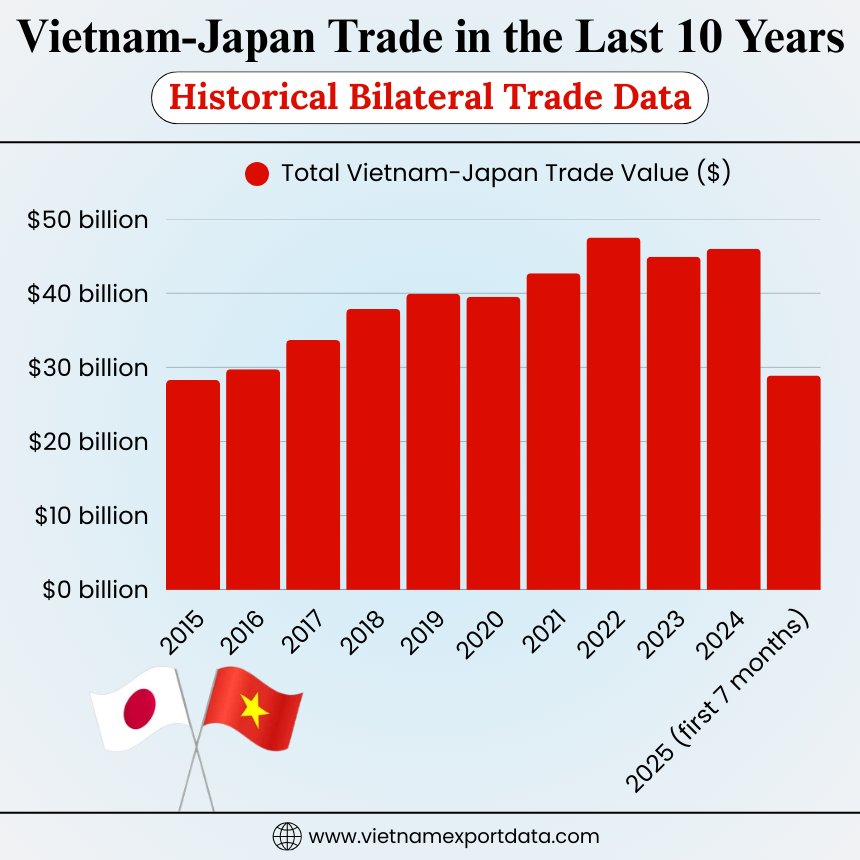
Vietnam-Japan Trade in the Last 10 Years: Historical Bilateral Trade Data
|
Year of Trade |
Total Vietnam-Japan Trade Value ($) |
|
2015 |
$28.28 billion |
|
2016 |
$29.76 billion |
|
2017 |
$33.70 billion |
|
2018 |
$37.87 billion |
|
2019 |
$39.95 billion |
|
2020 |
$39.53 billion |
|
2021 |
$42.71 billion |
|
2022 |
$47.53 billion |
|
2023 |
$44.92 billion |
|
2024 |
$46 billion |
|
2025 (first 7 months) |
$28.90 billion |
Sectoral Interdependence: How the Supply Chain Works
Vietnam–Japan trade is not a simple exchange of finished goods. It is best understood as a production ecosystem.
-
Japan supplies capital goods, technology, and materials
-
Vietnam assembles, processes, and manufactures
-
Finished goods are exported back to Japan or onward to global markets
This structure explains why:
-
Trade volumes are resilient
-
Investment and trade reinforce each other
-
Policy stability matters more than short-term price changes
VJEPA: The Policy Backbone of Trade Relations
1. Scope and Coverage
On December 25, 2008, Vietnam and Japan signed the Agreement for an Economic Partnership (VJEPA), which became operative on October 1, 2009. In contrast to the terms of the Agreement for Comprehensive Economic Partnership ASEAN-Japan (AJCEP), this is Vietnam's first bilateral free trade agreement (FTA) with Japan. But VJEPA does not take the place of AJCEP. The Vietnam–Japan Economic Partnership Agreement covers:
-
Trade in goods
-
Trade in services
-
Investment protection
-
Movement of business persons
-
Intellectual property
-
Customs facilitation
It was Vietnam’s first comprehensive bilateral economic partnership with a major developed economy.
2. Tariff Elimination and Market Access
Under VJEPA:
-
Japan is committed to eliminating tariffs on approximately 96% of tariff lines.
-
Vietnam is committed to eliminating tariffs on around 90% of Japanese tariff lines.
By the mid-2020s, most tariff reductions will be fully implemented or nearing completion.
For Vietnamese exporters, this has meant:
-
Lower landed costs in Japan
-
Improved competitiveness against non-FTA suppliers
-
Better access to processed goods and industrial products
3. Rules of Origin and Compliance
VJEPA’s rules of origin are relatively flexible compared to older FTAs. This allows:
-
Use of regional inputs
-
Cumulation within supply chains
-
Easier compliance for manufacturers operating across Asia
For sectors like textiles and electronics, this has been critical.
4. Investment and Services Impact
Beyond goods trade, VJEPA has:
-
Encouraged Japanese FDI in manufacturing, infrastructure, and services
-
Improved investor confidence through legal protections
-
Supported technology transfer and skills development
Japanese investment has played a key role in upgrading Vietnam’s industrial capabilities.
Challenges Facing Vietnam–Japan Trade
Despite strong fundamentals, several challenges remain:
-
Rising competition from other Asian suppliers
-
Higher labor costs in Vietnam compared to earlier decades
-
Increasing technical and sustainability requirements in Japan
-
Exposure to global economic cycles
Meeting Japan’s evolving standards on sustainability, traceability, and digitalization will require continuous upgrading.
Opportunities Looking Ahead to 2025 & Beyond
Key opportunity areas include:
-
Higher-value electronics and precision components
-
Processed and branded agricultural products
-
Green and sustainable manufacturing
-
Services linked to exports, IT, and digital trade
Vietnam’s ability to move up the value chain will determine the evolution of trade over the next decade.
Conclusion: A Partnership Built for the Long Term
In conclusion, Vietnam–Japan trade relations in 2025 reflect depth, balance, and resilience. With over USD 46 billion in annual trade, diversified product flows, and a strong policy foundation under VJEPA, the partnership is well-positioned for sustained growth. Vietnam’s expanding manufacturing capabilities and Japan’s technological leadership continue to complement each other. As long as both sides invest in quality, innovation, and regulatory alignment, Vietnam–Japan trade will remain one of Asia’s most stable and strategically important bilateral relationships.
For more information on the latest Vietnam trade data, or to search live Vietnam import-export data by country, visit VietnamExportdata. Contact us at info@tradeimex.in for customized trade reports and market insights.
Share
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0